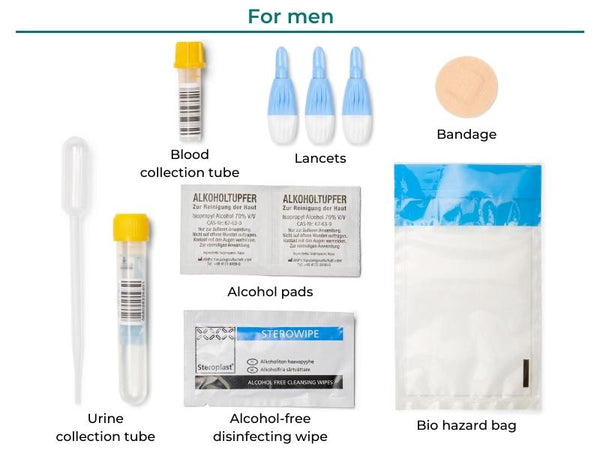
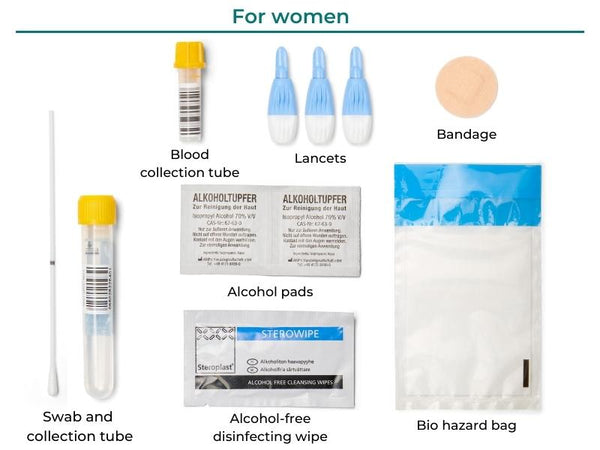
What is an STI?
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) are diseases that are transmitted through sexual contact. You can be infected with or pass on a virus or bacteria to someone else during sex. This can be through the penis, vagina, anus, and sometimes also with your mouth or fingers. Many STIs cause little or no symptoms. However, if they go untreated for long periods of time they can cause damage to the body. It is therefore important that you get tested if you have been at risk to treat the infection and to prevent it from spreading to others.
What is chlamydia?
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis. This bacteria can cause an infection of the urethra, cervix, rectum or throat. Chlamydia is transmitted through vaginal, anal, and oral sex or contact with infected genital fluids. Left untreated, the infection can spread to the epididymis in men, and to the uterus or fallopian tubes in women. This increases the risk of infertility or an ectopic pregnancy. A chlamydia infection during childbirth can lead to an eye infection and respiratory infection in the baby. Chlamydia is a very common STI and is treatable with antibiotics.
What is gonorrhoea?
Gonorrhoea is a highly contagious sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Not everyone with gonorrhoea develops symptoms, making early detection difficult. If left untreated, gonorrhoea can cause further health problems. In women, untreated gonorrhoea can cause pelvic inflammatory disease or infertility. In pregnant women, inflammation of the uterus, preterm birth, and ectopic pregnancy can occur. Pregnant women with gonorrhoea can also infect their baby during childbirth. This can lead to eye inflammation and blindness in the baby. In men, untreated gonorrhoea can cause inflammation of the epididymis or prostate.
In rare cases, gonorrhoea can enter the bloodstream and cause infections in other parts of the body. This can lead to joint inflammation, blood poisoning, or meningitis. Gonorrhoea is treatable with antibiotics.
What is trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. Although the symptoms vary, most people do not experience any symptoms and do not know they are infected. Trichomoniasis can cause inflammation of the vagina, cervix and urethra and make you more susceptible to other STIs. In pregnant women, infections with trichomoniasis are associated with preterm delivery and low birth weight. Trichomoniasis is treatable. To prevent re-infection, all sex partners should be treated at the same time.
What is Mycoplasma genitalium?
Mycoplasma genitalium (MG) is a bacteria that can be transmitted through unprotected oral, anal, or vaginal sexual contact. Research has shown that MG is common- while the exact prevalence of this STI is not known, a recent study found MG occurred more often than gonorrohea in a sample of patients. As many people do not experience any symptoms during an MG infection and it is not regularly tested for, most infections go undetected. In fact, more than 90% of men and 50% of women with an MG infection have no symptoms. Despite its lack of symptoms, MG can cause inflammation in the urethra, cervix, and fallopian tubes. MG is treated with antibiotics, although in some cases the infection spontaneously clears on its own. Antibiotic resistance is common in MG and specific considerations should be made when treating it.
What is syphilis?
Syphilis is a bacterial infection spread through sexual contact and is caused by the bacteria Treponema Pallidum. Syphilis can be transmitted through sexual intercourse or oral sex, infecting the penis, vagina, anus, or throat. Syphilis often produces no symptoms, although in the early stages of the infection it may cause a lesion (ulcer or chancre) where the syphilis entered the body. The bacteria infects the mucous membranes of the penis, vagina, anus, or mouth and can cause inflammation and rashes. Untreated syphilis can also suddenly make you sick after months or years without any symptoms. In rare cases, serious damage to the brain or heart can occur due to untreated syphilis. Syphilis can be detected with a blood test. It is easily treated with antibiotics if caught early.
What is HIV?
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a virus that attacks the body’s immune system. The virus is present in blood, semen, vaginal fluid, and breast milk, and can be contracted if these fluids enter your bloodstream. HIV is usually transmitted through anal or vaginal sex or sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injecting equipment.
You may not have many symptoms of HIV at first, you may be infected for years before you develop noticeable symptoms. Over time, however, your body’s immune system will decline, making you susceptible to many types of illnesses. This can lead to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), a chronic and life-threatening condition if left untreated.
HIV can be detected with blood tests. HIV cannot be cured, but AIDS can be prevented through proper detection and treatment. Timely and intensive treatment with various medicines can make the blood “virus-free”, so that someone is no longer contagious and has a normal life expectancy.
![Woman in professional cozy kitchen with Homed-IQ test kit]() 1
1![]() 2
2![]() 3
3![]() 4
4